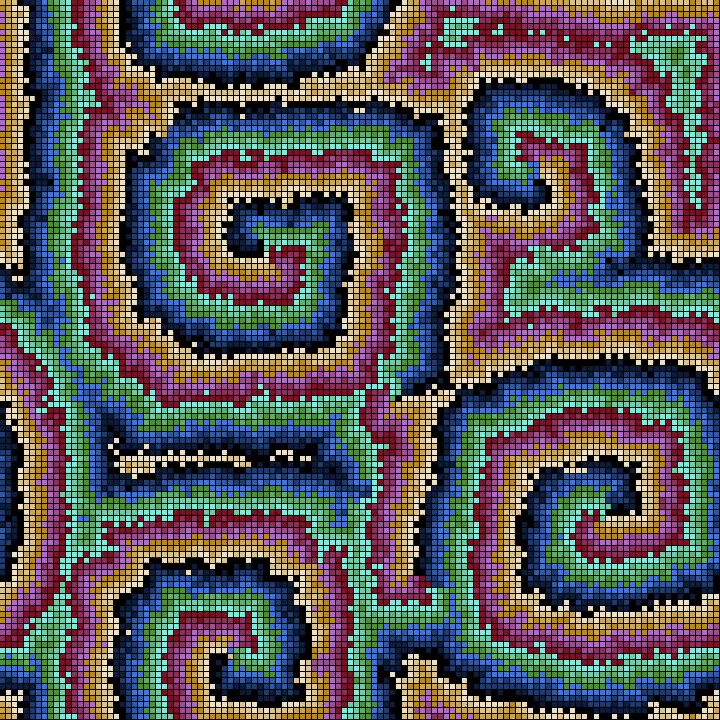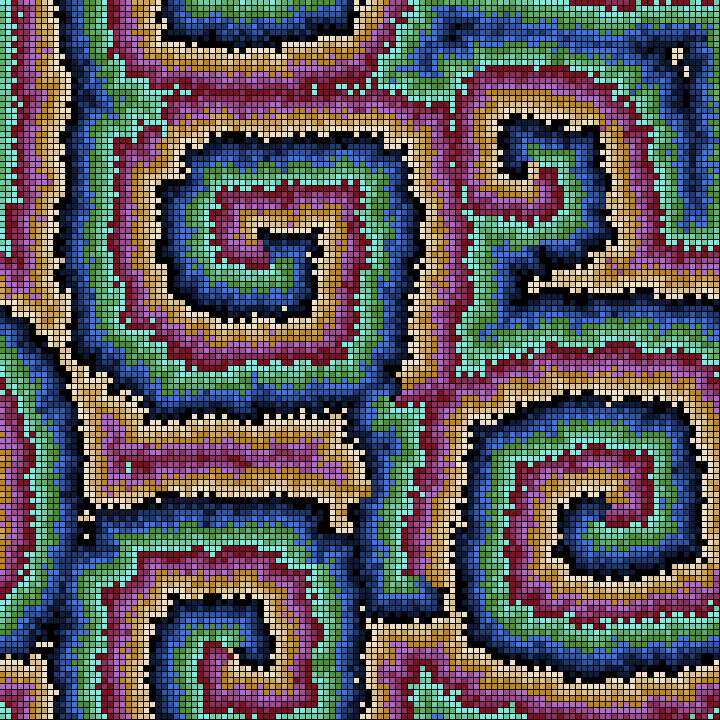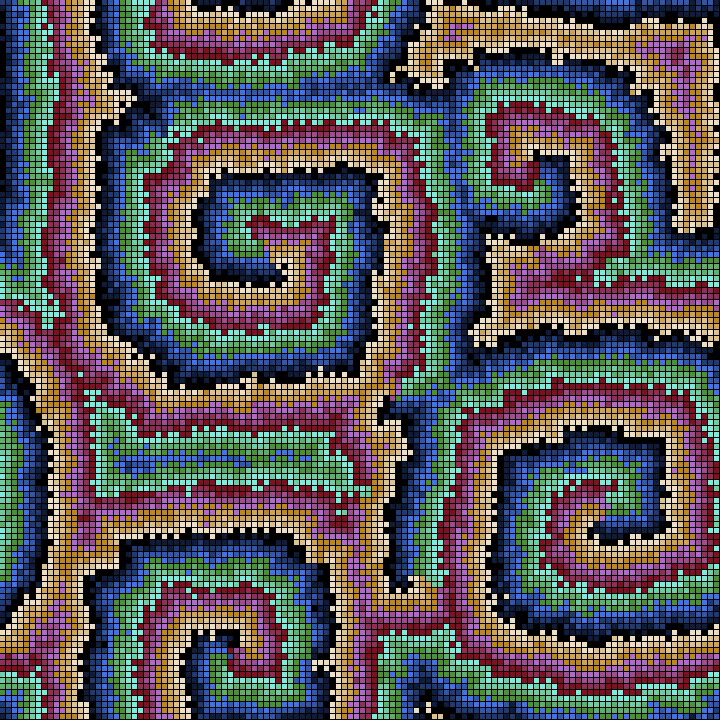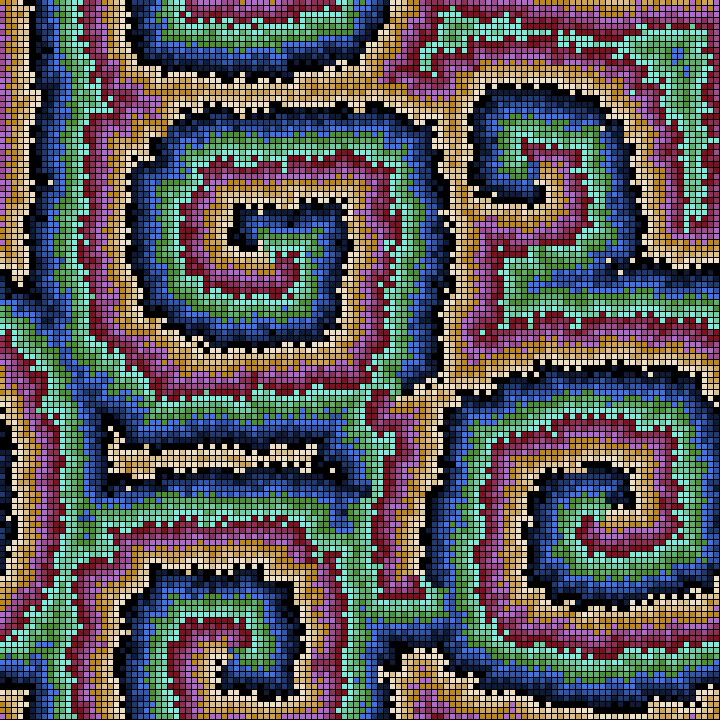
Cellular Neural Networks or Cellular Nonlinear Networks (CNN) are similar to Cellular Automata (CA): a grid of cells that evolve in time with local interactions with neighbouring cells.
Instead of a finite number of states for each cell (as for the CA) in CNN the cells can assume continuous values given from a chaotic oscillator and the local interactions are due to the coupling of oscillators in neighbouring cells.
With CNN is possible to model a number of physical systems described by Partial Differential Equations: Wave propagation, Heat Diffusion, Chemical Reaction-Diffusion and the likes.
In this case we have a Lorenz chaotic oscillator on each cell coupled with the 8 neighbouring oscillators.
The initial conditions, boundary conditions and coupling constant are chosen in such a way to obtain symmetrical patterns.
Here the CNN is rendered as a surface with a colormap from matplotlib (twilight).
The rendering is by means of a C++ program with openFrameworks toolkit.
https://objkt.com/asset/hicetnunc/639680